A Greener Path: Eco-Friendly Asphalt Maintenance Strategies

Key Takeaways
- Asphalt maintenance is essential for durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Sustainable practices are becoming increasingly crucial in asphalt management.
- Emphasizing the balance between innovation and environmental responsibility.
Introduction
Asphalt surfaces are fundamental to our road systems, providing a smooth, durable foundation for vehicles and pedestrians alike. It is estimated that over 90% of the roads in the United States are paved with asphalt, highlighting its prominence in infrastructure. This ubiquity is responsible for maintaining these surfaces sustainably and ensuring they remain safe and functional for years. Sustainable practices in construction and maintenance address the challenge of balancing functionality with environmental stewardship. Engaging with an asphalt contractor la porte in local areas can ensure that maintenance is carried out effectively, utilizing the latest eco-friendly techniques.
The Importance of Asphalt Maintenance
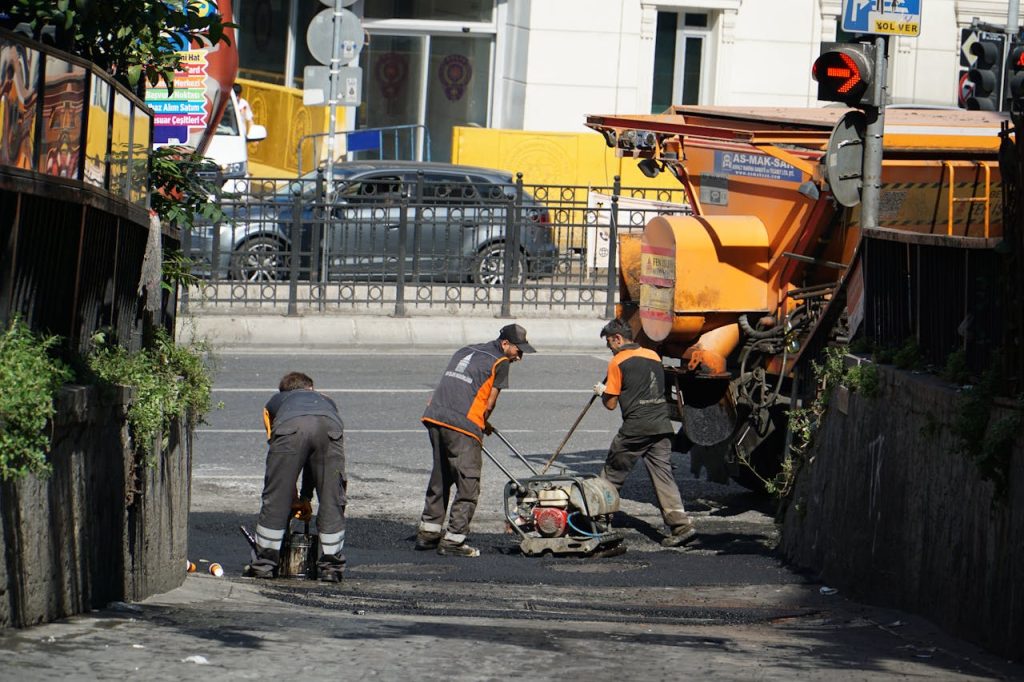
The emphasis on asphalt maintenance arises from its critical role in extending the lifespan of roads, minimizing expenses, and ensuring safety. Asphalt is prone to various stressors, including weather conditions, traffic load, and chemical exposure. Over time, these can cause significant deterioration, leading to safety hazards and increased repair costs. Minor issues can be avoided before they become substantial fixes with routine maintenance. Sealcoating, crack sealing, and regular inspections are just some techniques that can help maintain the integrity of asphalt surfaces. Ultimately, investing in consistent maintenance translates to enhanced infrastructural resilience and financial savings, as it significantly reduces the frequency and cost of complete overhauls.
Common Asphalt Issues and Solutions
Despite its durability, asphalt is not immune to damage. Common issues include potholes, cracks, and drainage problems, which can compromise the surface’s integrity and safety. Potholes, often caused by water infiltration and freeze-thaw cycles, are notorious for damaging vehicles and increasing the risk of accidents. Cracks can result from thermal fluctuations, heavy loads, or subpar installation. Implementing strategies such as hot and cold patching for potholes, crack filling, and proper drainage systems are vital for prolonging the surface’s life. Timely interventions can significantly reduce the escalation of damage, underscoring the importance of having a proactive maintenance plan.
Sustainable Practices in Asphalt Maintenance
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, the construction industry is shifting towards sustainable practices. Asphalt maintenance means utilizing recycled materials like reclaimed pavement (RAP), which minimizes waste and reduces the demand for new materials. Techniques such as cold in-place recycling (CIR) and warm-mix asphalt (WMA) involve less energy, release fewer emissions, and enhance pavement life by enhancing material performance. These methods are a more significant trend toward environmentally conscious and financially viable sustainable construction projects. By incorporating these methods, the industry can reduce its carbon footprint while improving the quality and longevity of the infrastructure.
The Role of Technology in Modern Asphalt Solutions
Asphalt maintenance is changing dramatically due in large part to technology. Innovations such as intelligent asphalt, which can adapt to changing weather conditions, and embedded sensors that monitor traffic and surface integrity are becoming more common. These technologies provide real-time data, enabling proactive and precise maintenance interventions. Using drones for inspection and monitoring further enhances the precision of maintenance operations, minimizing human error and maximizing efficiency. By leveraging these technological advancements, we can achieve sustainable maintenance outcomes that are more effective and less intrusive, reducing environmental impact while ensuring optimal road conditions.